Constant refinement of USP and value proposition is one of the main principles of modern marketing and it has found a reflection in Market Access too. It is important for pharmaceutical and medical devices companies to know their customers’ perceptions, needs and expectations. To meet and satisfy the demand for specific information or clinical evidence and to assign a fair market price in ever changing and evolving healthcare evidence and Real World Data (RWE).
Closed Loop Marketing (CLM) is a marketing approach in which incorporates a number of techniques and methods aimed at enhancing customer’s (payers, prescribers, providers and other decision makers) reach and improving their interaction with representatives of a life sciences company. It is also the process by which a pharmaceutical industry develops marketing strategies and deploys them through one or more channels to reach their customers and gain a sound understanding of their behaviour and perceptions on presented evidence – the value story.
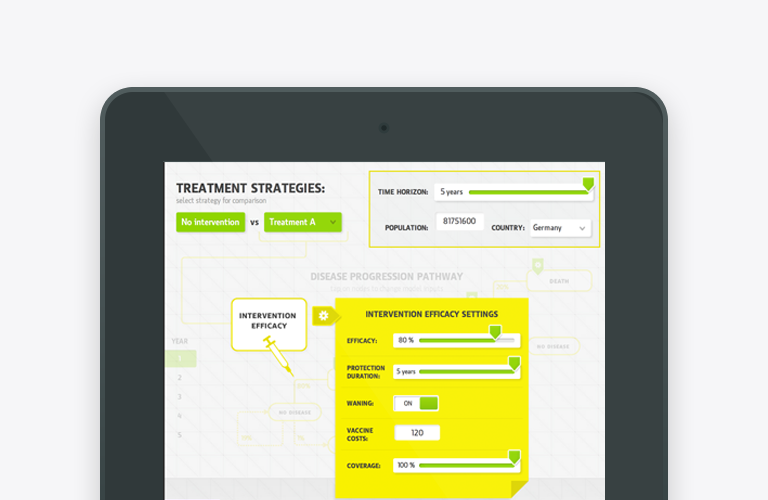
Today health economics models (budget impact, cost-effectiveness) are often transformed into interactive Web/iPad applications in order to improve model user experience and communication of modelled outcomes – the financial impact of adoption of a new healthcare technology.
Closed Loop Marketing can provide useful insights and data that can be used not only for marketing, but also for healthcare research purposes.
Understanding users’ behaviour and perceptions is essential for effective ongoing communication with healthcare payers and providers, as industry can shape the value story iteratively following analyses of real life insights from the field. Currently CLM techniques are integrated in various software packages available in the market or can be included in interactive model developments as optional module.
Main tasks of CLM can be formulated as follows:
- Gather detailed field level data from custom facing activities
- Analyse user actions and behaviour to transform data into insights for further value proposition refinement
- Understand real time usage to inform country support needs
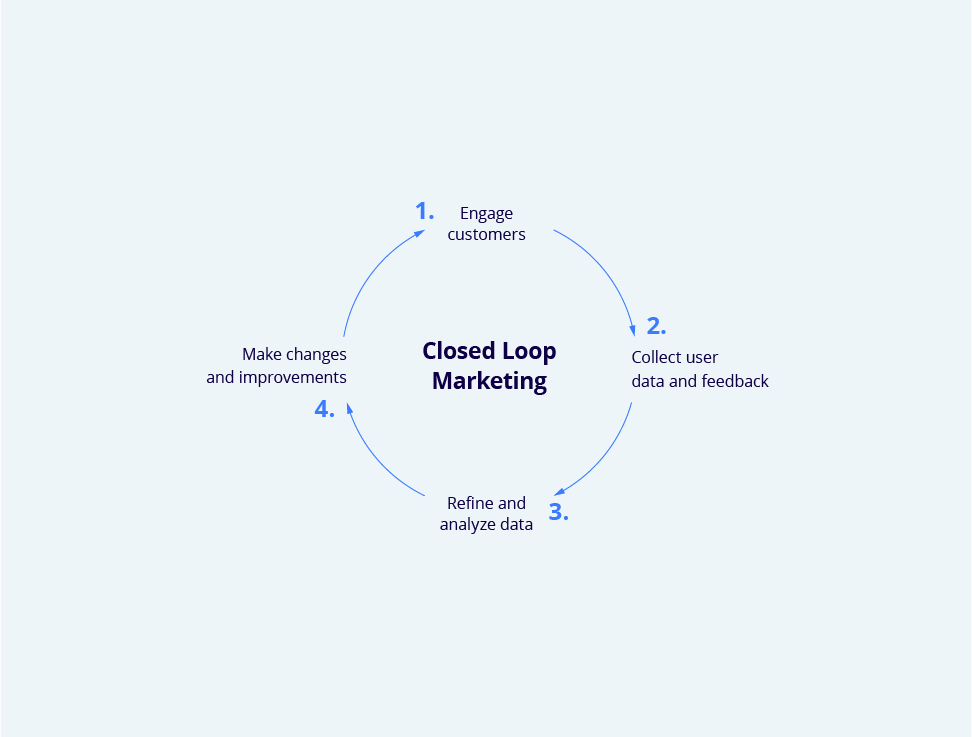
“Closing the loop” means passing the full circle of:
Engage customers > Collect user data and feedback > Refine and analyse data > Make changes and improvements > Engage customers
Figure 1. Closed Loop Marketing cycle
- Engage customers. This stage is usually characterized by a KAM visit to a customer. During customer facing KAM knows in advance customer needs, interests and patient profiles, with proper arguments fitted for customer settings – which in turn has been acquired from previous CLM cycle
- Collect user data and feedback. Collecting genuine and accurate data is always a challenge but proper tools can always give a hand with this issue. For instance, modern apps incorporate elements, which collect following data:
- Usage – number of presentations, average presentation time, CTR and other metrics
- Geography – Country/Region/City
- KAM name or territory coverage
- Customer name and post
- Content interaction. Timelines, charts, element/page views, heat maps – all measuring and illustrating user actions and interests in particular areas of the value story content.
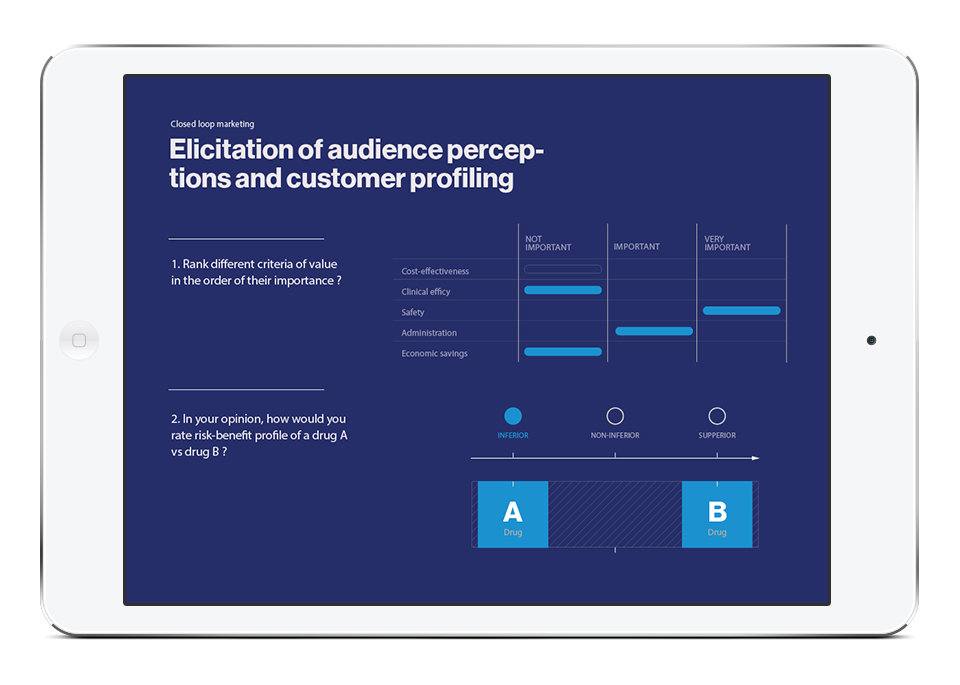
- Questionnaires. Consist of a few questions at the end of presentation and provide visit details data (overall satisfaction) and characterize willingness to pay
- Elicited data. Overall drug profile, perception of efficacy, prescription rates, direct medical costs and other data elicited during the visit
- Refine and analyse data. At this stage main actions are:
- Identify under-performing countries and/or regions
- Identify reasons and causes of poor performance
- Outline wrong messages and ineffective communication elements
- Make changes and improvements. Provide necessary support and training to regional and local market access, improve value proposition, poor performance, correct poor or non resonating messages and replace ineffective communication elements with proper ones.
CLM enables setting up custom campaigns dedicated to tracking session events, user behaviour and profile details of budget impact models’ target audiences. Other important and useful information relates to specific user flow and behaviour patterns within the model, user acquisition channels, geography, time spent in particular model section, number of sessions, session duration, model views and other analytics metrics. This information allows to better understand payers’ perceptions and general interest in particular parts of the economic value story.
CLM often contains embedded questioners or interface elements designed to record reaction, the service may provide data and insights required to continuously refine and upgrade an economic model to reflect real world payers’ perceptions. With custom events settings CLM tools can track particular actions taken by the user, for example, configure a model to track every +/- 20% cost data deviation from the base case value or track any modification of drug acquisition costs and efficacy values.
CLM also provides powerful tracking tools that allow to understand what data was changed and what were the input values entered by decision makers at the level of particular country, hospital setting or payer type. Testing of various input data scenarios and the extent of variability from base case parameters highlight areas where national estimates (based on national averages) are not representative, requiring further tailoring to local cost and epidemiology data.